|
Typically, the term 'cogeneration' in power systems
describes the use of steam for both power generation and heating.
High-temperature, high-pressure steam first passes through a turbine
to produce power. Normally in a simple-cycle power plant (i.e. NOT
cogeneration), any remaining energy in the steam would be dissipated
to the atmosphere or might even require additional energy to cool
(it’s usually allowed to expand in the turbine to the lowest
possible pressure and then discharged to a condenser to be converted
back into water).
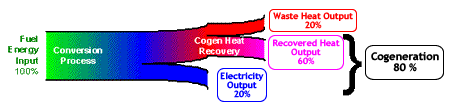
In a cogeneration system, this low-grade energy
is put to use. The low-pressure steam that exits the turbine is
used for such things as heating buildings, cooking food, boiling
wood pulp at a mill, or even heating domestic water for showers
in a dormitory. Energy efficiencies can be greatly improved with
cogeneration.
Basic Power Plant (NOT Cogeneration)

Cogeneration Power Plant
Topping and Bottoming Cycles
Cogeneration technologies are classified as
“topping-cycle” and “bottoming-cycle” systems.
These terms are relative to the steam turbine: does the heat
recovery occur 'before' the steam turbine(topping), or 'after' the
steam turbine (bottoming)?
In a typical topping-cycle system, you'll
find a gas turbine with a heat recovery steam generator, 'before'
the steam turbine. You can increase the thermal efficiency of a
steam electric generating system by increasing temperatures and
interposing a device, such as a gas turbine, between the heat source
and the conventional steam-turbine generator to convert some of
the additional heat energy into electricity.
In a typical bottoming-cycle system, energy
is recovered from the system 'after' the steam turbine.
The heat engine in a bottoming cycle would be a condensing turbine
(similar in principle to a steam turbine but operating with a different
working fluid at a much lower temperature and pressure).
So cogeneration isn't that complicated, after all.
Let's do a quick recap of this section, and then we can move onto
the Generator.
|