|
Gas turbines are most commonly found in a stand-alone configuration
(sometimes called ‘simple cycle’). In warm climates, all
you need to prepare is a concrete slab as a foundation and the turbine
is ready to generate power (almost ‘right out of the box’).
Below is a diagram of a gas turbine in a typical enclosure. The
turbine itself is made by the manufacturer, but a second company
usually adds a generator and packages it inside a specially developed
enclosure. This enclosure usually has air filters, vibration protection,
electrical grounding, lubricating systems, a starting motor and
fire suppression equipment.
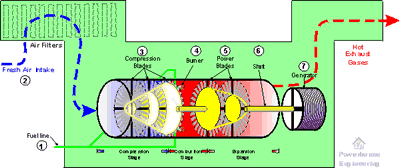
1. The fuel goes
in (in this case, itís natural gas).
2. Fresh, combustion air is added. It goes through some filters to remove
any dust or other impurities.
3. The fresh air is compressed by the first set of blades.
4. The fuel is burned in the combustion chamber.
5. Burning the fuel creates a lot of expanding gases, which flow through the
power blades, causing the turbine to spin.
6. The spinning turbine is attached to a generator, which also spins.
7. The generator creates electricity.
A typical, simple-cycle turbine package like this can achieve
efficiencies of 37% (LM2500) to 40% (LM6000). Now letís see a gas turbine
installed in cogeneration mode.
|